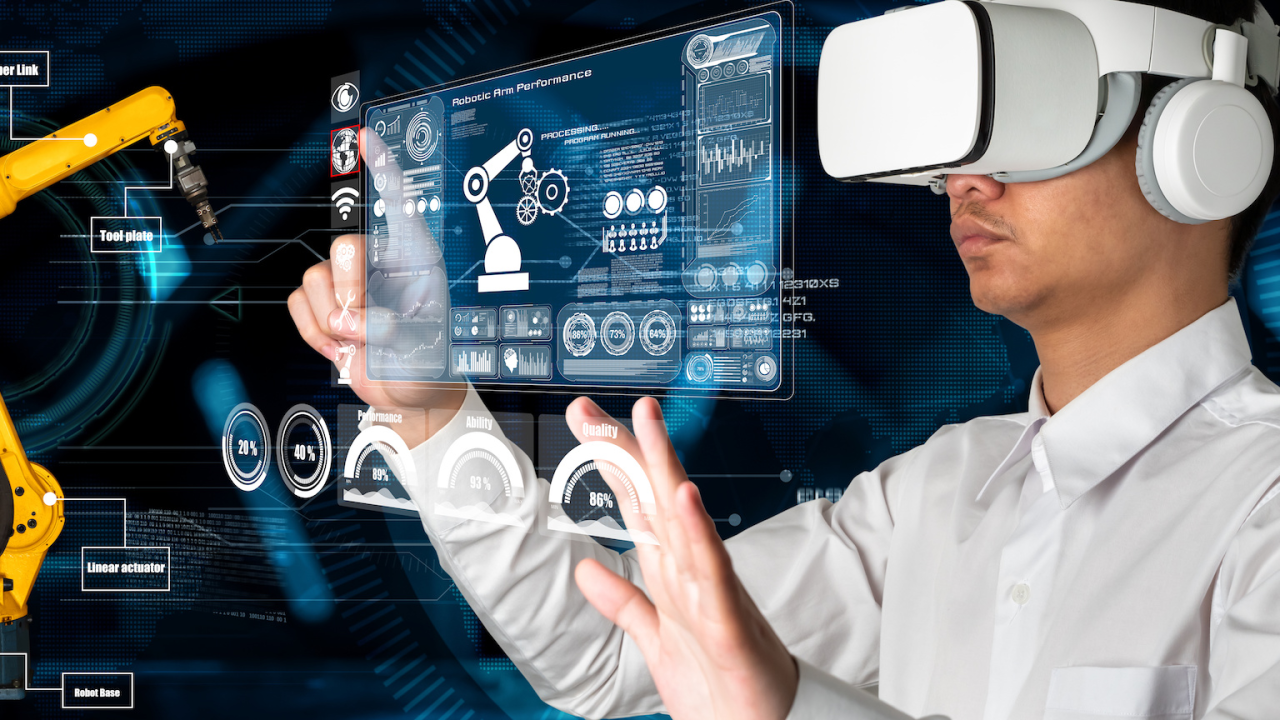
In recent years, Virtual Reality (VR) has evolved from a futuristic concept into a transformative technology that is reshaping how we interact with digital environments. What was once confined to the realm of science fiction is now at the heart of industries ranging from entertainment to healthcare. VR is revolutionizing the digital experience, offering users an immersive world that extends far beyond traditional screens and devices.
This article explores how VR is influencing digital spaces, the key industries adopting it, its benefits, challenges, and what the future holds. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or simply curious about the technology, this comprehensive guide will help you understand why VR is such a big deal in the digital age.
What Is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality refers to a simulated environment generated by a computer that immerses the user in a 3D space. Unlike traditional user interfaces, VR places the user inside the experience. By simulating as many senses as possible — including vision, hearing, touch, and even smell — the computer transforms the user into part of this virtual world.
VR systems typically include:
A. A Head-Mounted Display (HMD)
B. Motion tracking sensors
C. Hand controllers
D. Sometimes external tracking cameras or gloves
These components work together to monitor the user’s movements and adjust the virtual environment accordingly, creating a fully immersive digital experience.
The Evolution of Virtual Reality Technology
The concept of VR dates back to the 1960s with early prototypes like the “Sword of Damocles” headset. However, significant progress has occurred only in the last decade due to advancements in:
A. Graphics processing units (GPUs)
B. Display resolution
C. Sensor accuracy
D. Artificial Intelligence integration
E. Cloud computing
Companies such as Oculus (now part of Meta), HTC, Sony, and Valve have made VR more accessible and affordable, allowing broader adoption across different markets.
Key Industries Being Transformed by VR
A. Gaming and Entertainment
VR has had the most noticeable impact in the gaming world. With popular titles like Beat Saber, Half-Life: Alyx, and VRChat, users can engage in immersive gameplay that makes traditional gaming feel flat in comparison.
VR in entertainment also extends to:
-
Virtual concerts
-
Immersive cinema experiences
-
VR theme parks and attractions
B. Education and Training
VR is revolutionizing the education sector by offering interactive learning experiences. Students can explore historical events, dissect virtual animals, or even conduct complex chemistry experiments in a safe digital lab.
Training applications include:
-
Medical surgeries
-
Flight simulation for pilots
-
Military combat training
-
Emergency response drills
C. Healthcare and Therapy
Medical professionals use VR for diagnosis, surgery planning, and even treatment. VR is also widely used in:
-
Pain management
-
Physical therapy
-
Exposure therapy for PTSD and phobias
-
Autism spectrum disorder therapies
D. Real Estate and Architecture
Through VR, potential buyers can take 360-degree tours of homes without physically visiting them. Architects use VR to simulate how a building will look and feel before construction even begins.
Benefits include:
-
Reduced travel costs
-
Faster decision-making
-
Better design visualization
E. E-Commerce and Retail
E-commerce platforms are exploring VR to provide a more engaging shopping experience. Imagine trying on clothes or walking through a virtual store from your home.
VR in retail helps:
-
Increase customer engagement
-
Reduce return rates
-
Boost brand loyalty
F. Tourism and Travel
Tourism boards and travel agencies use VR to offer “virtual vacations” or previews of real destinations. This can influence travel decisions and promote places that are otherwise hard to reach.
Benefits of Virtual Reality
A. Deep Immersion
VR’s primary strength lies in its ability to create a sense of presence, making users feel like they are truly part of the digital world.
B. Better Engagement
Immersive experiences often lead to higher retention rates, making VR an excellent tool for training, education, and marketing.
C. Cost and Time Efficiency
Training in VR can reduce risks and costs associated with real-world training environments.
D. Enhanced Creativity
From art and design to storytelling and marketing, VR offers a canvas where creativity is limitless.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, VR still faces several challenges that slow down its mainstream adoption.
A. High Costs
While prices have dropped, high-quality VR headsets and compatible systems are still relatively expensive for the average consumer.
B. Motion Sickness
Many users experience nausea or discomfort due to latency issues or disorienting virtual movements.
C. Content Scarcity
Developing VR content is resource-intensive, and the market still lacks a wide range of high-quality, interactive experiences.
D. Technical Limitations
VR depends heavily on hardware. A powerful PC or gaming console is often required, and wireless options still have limitations in battery life and performance.
E. Privacy Concerns
With VR collecting large amounts of personal data (eye movement, spatial movement, and even biometrics), privacy is a growing concern that needs strict regulation.
The Role of VR in Remote Work
The global shift to remote work has opened new opportunities for VR to redefine collaboration. Virtual meeting rooms, interactive whiteboards, and 3D workspaces are becoming the norm for teams spread across different geographies.
Benefits include:
A. Improved team collaboration
B. Real-time interaction with 3D models
C. Less fatigue compared to traditional video calls
D. Better training and onboarding experiences
Companies like Meta (with Horizon Workrooms), Spatial, and Microsoft (with Mesh for Teams) are pioneering this transformation.
Future Trends in Virtual Reality
Looking ahead, several trends suggest VR will become even more integral to our digital lives:
A. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Combining VR with AI enables smarter environments that adapt in real-time based on user behavior, making experiences more personalized.
B. Wireless and Lightweight Devices
As technology advances, expect smaller, wireless headsets with higher resolution and longer battery life to become standard.
C. Social VR
Platforms like VRChat, AltspaceVR, and Meta Horizon Worlds are creating entirely new ways to socialize and build communities in virtual spaces.
D. Mixed Reality (MR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
The lines between VR, AR, and MR are blurring. Devices like Apple Vision Pro and Microsoft HoloLens are merging the physical and digital worlds.
E. VR in the Metaverse
The concept of a unified digital universe — the Metaverse — is still in development, but VR is at its core. As more businesses invest in virtual worlds, VR will play a pivotal role in shaping this future.
How Businesses Can Prepare for the VR Revolution
For businesses looking to leverage VR, it’s essential to begin planning now. Here’s how:
A. Identify areas where VR can add value (training, product design, customer experience)
B. Invest in employee training and infrastructure
C. Collaborate with VR developers for custom solutions
D. Stay updated on VR trends and standards
Being an early adopter can lead to a significant competitive advantage as VR adoption grows.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality is no longer just a novel concept — it is a powerful tool reshaping how we experience the digital world. From gaming and entertainment to education, healthcare, and business, VR offers immersive experiences that are more engaging, efficient, and impactful than traditional digital interfaces.
As the technology continues to evolve, the potential for VR is virtually limitless. Businesses, educators, healthcare professionals, and even governments must start exploring the opportunities it presents today. The digital future is immersive, and VR is leading the charge.